Reduce food waste in your restaurant
Kikleo is the leading partner to help you reduce
your waste thanks to its innovative food waste analysis technology.
Reduce sustainably waste eating in your restaurant
Kikleo is the leading partner to help you reduce your waste thanks to its innovative food waste analysis technology

With our standalone solution, our clients have achieved significant savings
meals saved from the trash
of CO2 eq avoided
saved
food waste reduction



Reduce post-consumer waste
You are equipped with a conveyor: our Conveyor Scan analyzes and measures food waste in the room thanks to the automatic scanning of trays on the conveyor.
-
Ideal for restaurants equipped with a conveyor belt
-
Differentiation of all types of food
-
Easy and quick plug & play setup

Reduce post-consumer waste
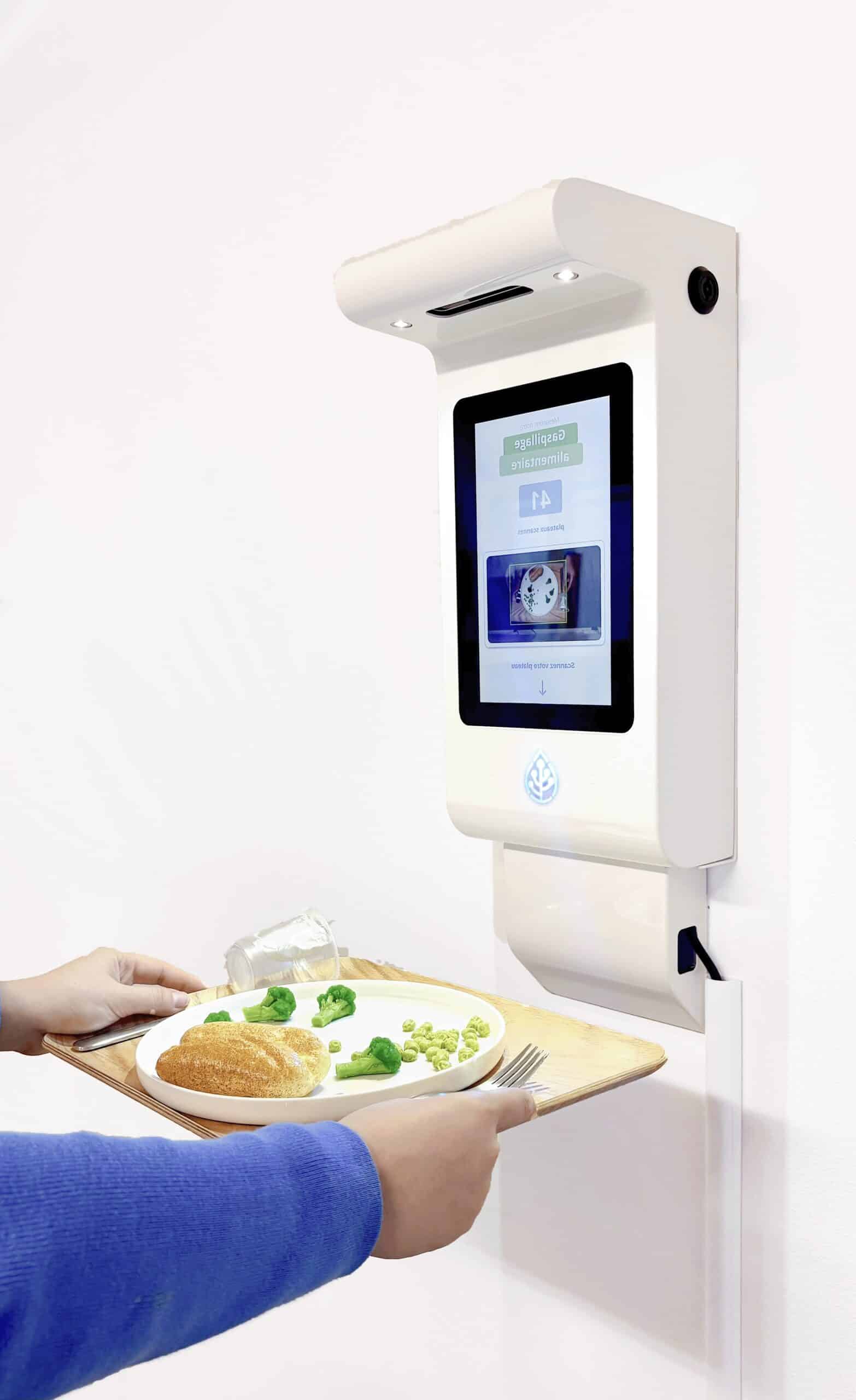
Our Guest Terminal identifies and estimates the quantity of each food item left on the guests' trays or plates.
-
Adaptable to any type of restaurant
-
Simple installation on a table, sorting table or directly on the wall
-
Easy and quick plug & play setup
-
Autonomous analysis without team intervention

Reduce the waste indoors
Thanks to artificial intelligence, our camera detects, identifies and estimates the quantity of each food item left on the trays or plates of the guests.
-
Adaptable to any type of restaurant
-
Simple installation on conveyor or sorting table
-
Easy and quick plug & play setup
-
Autonomous analysis without team intervention



Reduce pre-consumer waste
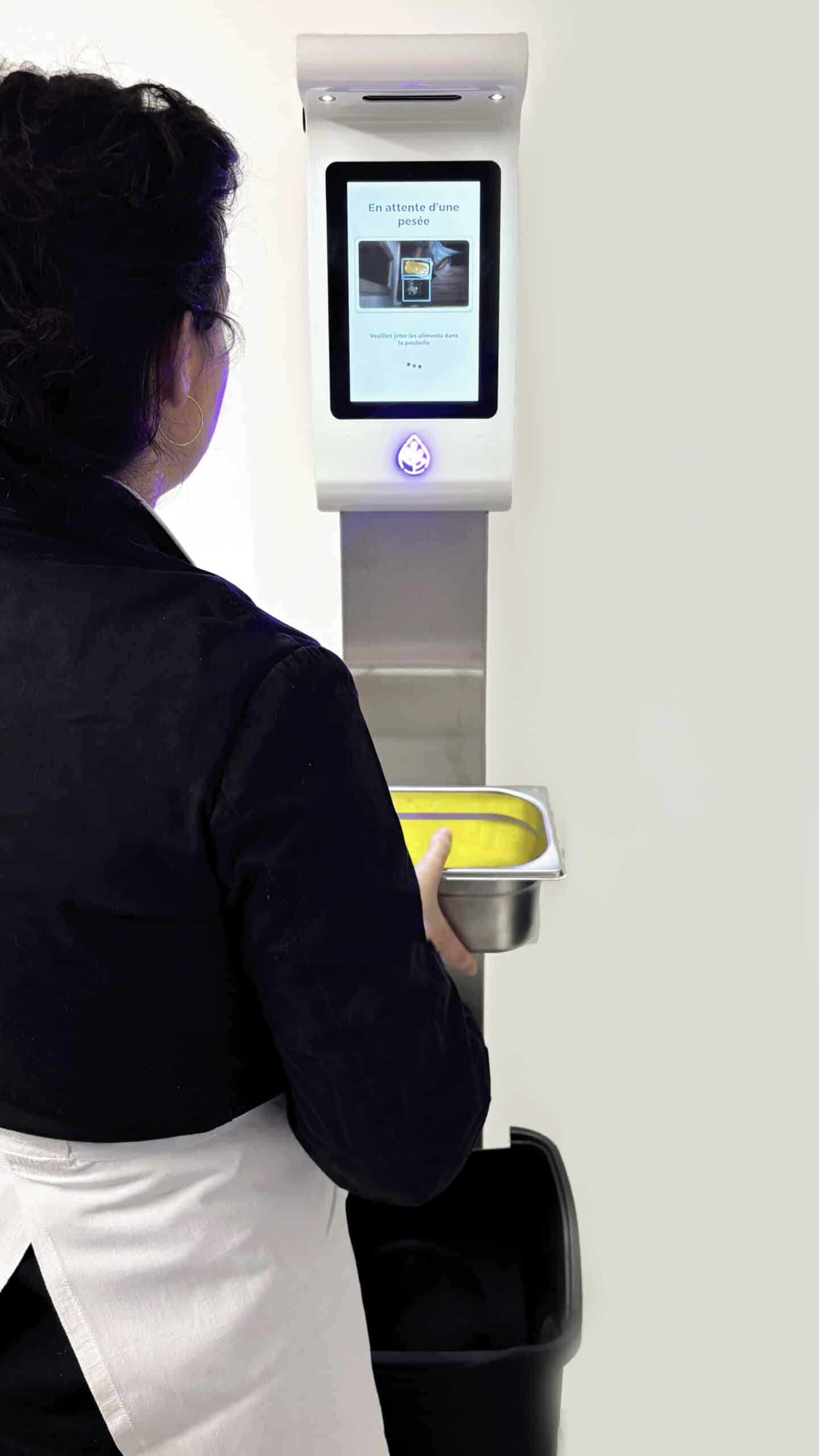
Our Kitchen Kiosk automates and digitizes the weighing process in the kitchen , for effortless food waste diagnosis by the teams.
-
Adaptable to any type of kitchen
-
Automated version with the Kikleo camera
-
Semi-automated version with the connected tablet
-
Differentiation of all types of food


Reduce waste kitchen
Our connected scale automates and digitizes the weighing process in the kitchen , for effortless food waste diagnosis by the teams.
-
Adaptable to any type of kitchen
-
Automated version with the Kikleo camera
-
Semi-automated version with the connected tablet
-
Differentiation of all types of food
You are ...
A school or university restaurant
A company or administrative restaurant
A hospital or healthcare facility
A hotel or any other tourist establishment
A connected platform to manage and track your food waste
Real-time monitoring of your restaurant
An overview of your economic losses
Modular data
Personalized action plans
Monitoring your environmental impact
A connected platform to manage and track your waste
Real-time monitoring of your restaurant
An insight into the cost of your waste
Modular data
Areas for improvement
Monitoring your environmental impact
Why choose Kikleo?
Beyond reducing food waste in your establishment, our solutions allow you to understand the consumption trends of your guests.
By analyzing your waste, you can implement relevant and effective action plans , improve the quality of your catering service and customer satisfaction